Aberration, in Physics Meaning
Socially, aberration is any action or fact that goes against the norms and cultural precepts that has a negative impact on the environment and/or causes damage in some way, meanwhile, in physics, it is a phenomenon that occurs in optical systems when the Light rays suffer unexpected deviations that cause the light not to focus on the proper focal point and produce distorted or blurry images.
In optical systems, aberrations are often present because no lens is perfect and deviations from the ideal case are inevitable. Aberration phenomena can be observed in telescopes, microscopes, cameras, etc. Even the vision defects that many of us suffer from are the result of aberrations that occur in the eye.
Example of aberration
Let us consider a convex lens on which light rays are incident perpendicularly and which are parallel to each other. The lens, having a certain refractive power, will deflect or refract these light rays and focus them on a point F located at a focal length D.
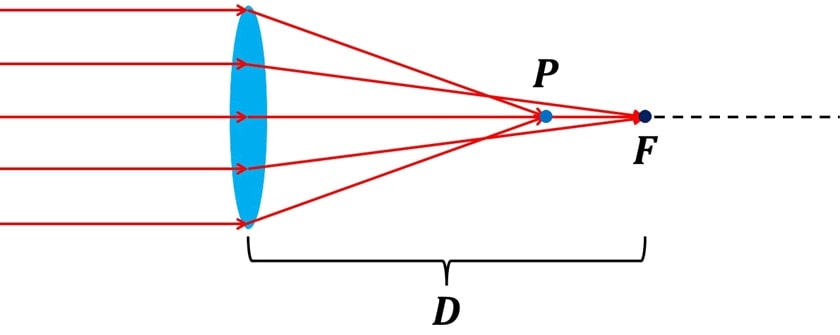
However, this is what would happen in the ideal case where you have a perfect lens, that is, one that refracts all light rays in the same way. In reality, no lens is perfect and what happens in this case is that the light rays that hit the ends of the lens will be refracted more and will be focused on another point P that is located on the same focal plane but is at a distance from the lens. different distance from point F. This is an example of a type of aberration known as “spherical aberration.”
Aberration classification
There are different types of optical aberrations depending on the case in which we find ourselves. These are:
Spherical aberration: This is the type of aberration we saw earlier. It occurs when the light rays incident on a spherical lens are refracted in different magnitudes and are focused at different points. Generally, rays incident at the ends of the spherical lens tend to refract differently than light rays incident closer to the center of the lens. This type of aberration produces blurry or distorted images.
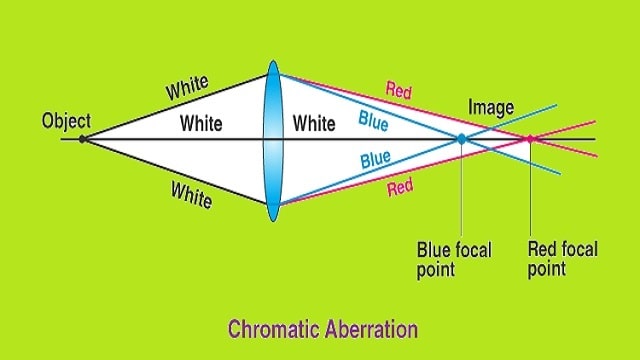
Chromatic aberration: In this type of aberration, light rays are refracted differently depending on their wavelength or frequency. In the case of visible light this means that different colors refract in different ways. We can observe this, for example, when white light falls on a prism and it refracts the colors to a different degree, resulting in the separation of the visible light spectrum.
Distortion aberration: Distortion aberration occurs when a lens has varying degrees of magnification across it. This causes the projected image to have distortions at the ends of it.
Coma aberration: This type of aberration occurs when there are light rays that do not fall perpendicularly on the lens, but rather strike at a different angle. This causes light rays to refract differently along the lens and the result is a distorted “comma”-shaped image.
Astigmatic aberration: In this type of optical aberration, the light rays that are in different focal planes are refracted with different magnitudes. This causes a variation in the focal length of each focal plane. Astigmatic aberration causes images to appear distorted in different focal planes.
Optical aberrations and vision defects
The human eye from a purely physical point of view can be considered as a camera with a lens system. The cornea and the lens are the two structures of the eye that act as lenses. They are responsible for refracting incident light and focusing it towards the retina, which is the photosensitive part of the eye and whose stimuli are sent to the brain to form an image.
However, small variations in the shape of the cornea or lens, or some defects in the general shape of the eye, can cause aberrations that cause light not to focus directly on the retina, but rather to do so at a point. different.
Myopia is a common vision condition that occurs when light incident on the eye is focused in front of the retina, causing distant objects to appear blurry. On the other hand, hyperopia is another vision defect that occurs when the light that falls on the eye focuses on a point that would be behind the retina. People with farsightedness have difficulty seeing close objects clearly.